What Is Forex Trading and How Does It Work?
 Fact-checked
Fact-checked
Last Updated: April 14, 2022
Forex trading is a lucrative market. But what is forex trading and how does it work? In this article, we discuss what forex is and how its market works. We also provide insight into what affects price movements, so you can anticipate your trades. What’s more, we provide a quick rundown on the types of markets you can enter and what currencies are best to trade.
What Is Forex Trading?
Forex trading (foreign exchange trading or FX trading) is the exchange of world currencies based on current market rates. You can trade any currency for another, but traders focus on only a handful of major currencies:
- US Dollar (USD)
- Euro (EUR)
- Japanese Yen (JPY)
- British Pound (GBP)
- Australian Dollar (AUD)
- Canadian Dollar (CAD)
- Swiss Franc (CHF)
Investing is generally a good idea, and forex investing is a top choice among investors. It occurs in the forex market, which is the most liquid financial market in the world. With an average daily trading volume of $5 trillion, the forex market is also the biggest financial market around.
Forex trading participants include traders, investors, institutions, and banks. When you visit a foreign country, you often need to exchange your currency with that country’s local currency—effectively making you a participant in the forex market.
| NOTE: The forex market’s average daily trading volume is much higher than the stock market and is much more liquid than any other financial market. |
How Does Forex Trading Work?
Forex trading occurs between two over-the-counter (OTC) parties since the fx market doesn’t have a centralized exchange location; so trading currency online is quite popular, thanks to a global network of banks and financial institutions.
Forex markets have a 24-hour operation, due to the overlaps in time zones across four major trading centers:
| Trading Center | Operating Time |
| London | 3:00 a.m. to 12:00 p.m. EST (8:00 p.m. to 5:00 p.m. UTC) |
| New York | 8:00 p.m. to 5:00 p.m. EST (1:00 p.m. to 10:00 p.m. UTC) |
| Tokyo | 7:00 p.m. to 4:00 a.m. EST (12:00 a.m. to 9:00 a.m. UTC) |
| Sydney | 5:00 p.m. to 2:00 a.m. EST (10:00 p.m. to 7:00 a.m. UTC) |
As one major trading center closes, another one opens. For traders, this results in a seamless all-day trading experience.
| NOTE: The overlap in the New York and London trading sessions is the busiest time in the forex market, accounting for the majority of its daily trading volume. |
What Influences the Forex Markets?
Profitable forex trading for beginners may sound difficult, but it’s easier if you know what influences the market.
Supply and Demand
Forex rates follow the law of supply and demand.
High demand for a country’s goods results in more exports than imports. The demand for the exporting country’s currency rises because buyers use the exporter’s currency to buy their goods, which increases the currency’s value. On the flip side, if the country imports more than it exports, there’s less demand for its currency, shrinking its value.
Central Banks
Central banks —such as the Federal Reserve (Fed) and the European Central Bank (ECB)—influence forex trading by implementing interest rate policies to control their economy.
If the economy weakens, central banks cut rates to stimulate spending, bolstering economic activity. If the economy is overheating and inflation is skyrocketing, people avoid spending. Central banks then increase rates to slow down growth and inflation.
How does this influence the fx market? Higher interest rate currencies are more attractive to foreign investors since they can accrue more returns. Lower interest rate currencies depreciate because fewer investors want to acquire them.
Understanding forex means understanding interest rate policies. And central bank actions crucially move the market.
News Reports
Traders keep their eyes and ears glued to the news for important reports about disasters, executive actions, and even stock market reports. A spew of critical news can adversely affect a country’s economic activity, which moves the forex market.
Economic Data
To learn forex trading, you also need to learn economic reports that show data on the economy’s activity.
For instance, US unemployment data is released every third Friday of the month. If the number of jobless people turns out to be more than anticipated, expect a huge movement in forex rates. This report also influences the central bank’s decision on interest rates—making it more important for traders to be attentive to it.
Credit Ratings
Countries have credit ratings that show risks of default, indicating how capable a country is in terms of paying its debts and loans. Put simply, low-rated countries typically have weaker currencies.
| NOTE: Foreign exchange trading is largely influenced by a handful of central banks, namely the Federal Reserve (the Fed), European Central Bank (ECB), Bank of England, and the Bank of Japan. |
Types of Forex Markets
You can categorize forex trading based on three markets: spot, forward, and futures.
Spot FX Market
Spot forex trading is the largest fx market where currencies exchange based on their spot trading price. Simply put, a spot fx deal happens ‘on the spot’.
Forward FX and Future FX Markets
In the forward fx market, a forex online trade is done under a private agreement between two parties to buy a currency at a future date at a pre-set price. The agreement and size of the contract are negotiable.
The future fx market is similar, except the size of the trade is standardized and the trade occurs on an exchange with clearing houses that guarantee the transactions.
Key Takeaways
| The forex market is the biggest and most liquid financial market in the world. |
| Forex trading happens when you exchange one currency for another based on an exchange rate. |
| Different factors influence the movement of currencies, including the actions of central banks, economic reports, and supply and demand. |
| There are three types of forex trading markets: spot, forward, and futures. |
Forex Trading Currencies
FX trades basics aren’t complete without discussing the currencies that make up the market. Unlike investing in cryptocurrency—where you typically buy and hold one digital currency—forex trades are done in currency pairs.
These pairs are made up of the base and quote currencies. In the EUR/USD currency pair, the EUR is the base currency and the USD is the quote currency. If the EUR/USD pair is at $1.22, for example, it means 1 EUR is equivalent to USD 1.22.
Major pairs have the biggest average daily trading volume in the forex market, as seen here, with their nicknames:
- EUR/USD (Fiber)
- USD/JPY (Yen or Ninja)
- GBP/USD (Cable)
- USD/CHF (Swissy)
- USD/CAD (Loonie)
- AUD/USD (Aussie)
- NZD/USD (Kiwi)
These pairs include ‘USD’. But how does forex trading work without the dollar? Major pairs without the dollar are called minor pairs or cross pairs. They include:
- GBP/EUR
- GBP/CAD
- EUR/AU
- AUD/NZD
- AUD/JPY
- CHF/JPY
- EUR/JPY
- NZD/JPY
If the pair consists of a major currency and an emerging market currency, they are considered to be exotic pairs, which include:
- EUR/TRY (Turkish Lira)
- USD/HKD (Hong Kong Dollar)
- JPY/NOK (Norwegian Krone)
- NZD/SGD (Singapore Dollar)
- GBP/ZAR – (South African Rand)
Exotic pairs also consist of pairs from a specific region, called regional pairs, such as AUD/NZD and EUR/NOK.
Bid and Ask Prices
To understand more about forex trading, it’s imperative to understand the concepts of bid and ask prices. The bid price is the price the dealer will pay for a currency, and the asking price is the rate at which they will sell it.
Suppose that the bid and ask price for EUR/USD are $1.40 and $1.30, respectively. You’ll pay $1.40 to buy one euro, and if you want to sell that euro, you’ll receive $1.30.
The difference in prices counts as the dealer’s profit, which is called the ‘spread’. Traders, of course, prefer currency pairs with thin bid-ask spreads.
| NOTE: The dollar has quite a few nicknames used by traders, the most popular ones are ‘buck’ and ‘greenback’. |
Forex Trading Charts
What is forex trading and how does it work in terms of analysis? Traders use various technical charts to analyze prices, including:
Candlestick Charts
Show the market’s opening, high, low, and closing prices for the day. It consists of a ‘real body’ that shows the opening and closing prices of the pair. It’s color-coded, with one color pertaining to a higher opening than the closing, and another color indicating a lower opening than the closing. The thin lines above and below the real body show the highest and lowest prices of the pair in the session, as seen below:
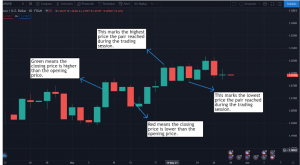
Bar Charts
Are the same as candlestick charts but thinner and simpler:
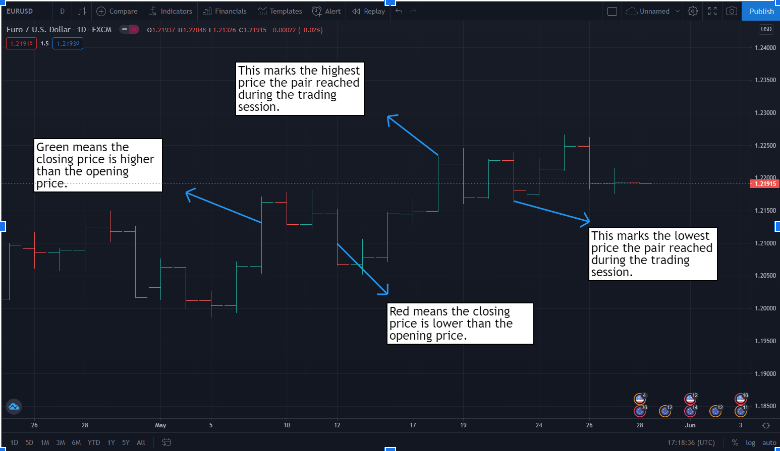
Line Charts
are used by traders to obtain quick forex information. A line is drawn from one closing price to another. Connected, they form a linear view of the general price movement of the pair:
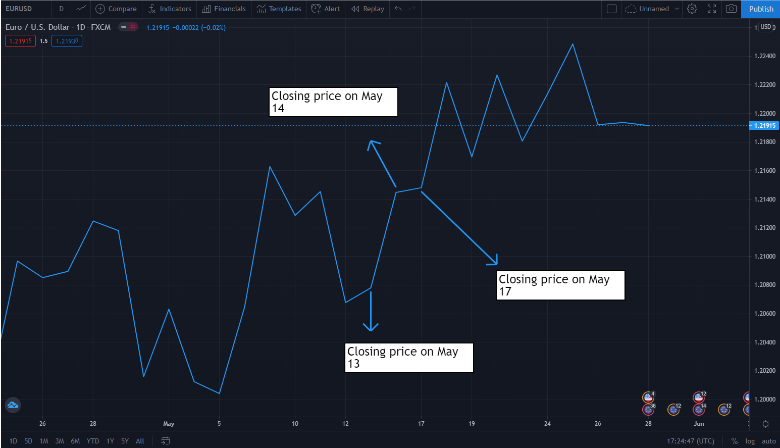
| NOTE: Traders use interesting nicknames for the chart patterns they observe, such as Head & Shoulders, Triangles, Engulfing, and Ichimoku Cloud Bounce. |
Forex Terminology
To avoid confusion when trading in the forex market, familiarize yourself with the following terminology:
Spread
The difference between the bid and ask prices.
Leverage
The use of borrowed funds to greatly profit from a small price change. As a crucial forex guideline, use leverage sparingly—it amplifies not only your profit but also your losses if the trade goes against you.
Lot
The size or amount of money you’re trading at the time.
Margin
Together with leverage, it’s the percentage of the size you control based on your forex position. For instance, if you’re trading $1,000 and you use a 1% margin, then you can control $10,000 worth of currency.
Pip
a standardized unit used to measure the smallest amount by which a currency pair can move. Its forex trading meaning can be ‘percentage in point’ or ‘price interest point’.
Long Position
Buying a currency pair that you expect to appreciate. For instance, having a long position on EUR/USD means you expect the value of the euro against the dollar to rise.
Short Position
When entering a short position, you expect the currency pair to depreciate. Having a short position on EUR/USD means you expect the euro to weaken against the dollar.
| NOTE: You can either be a bull or bear in forex trading. A bullish market means prices are rising, while a bearish market means prices are falling. |
Conclusion
The forex market is the biggest and most liquid financial market in the world. It’s decentralized and operates 24 hours a day, five days a week. How does forex trading work? Traders exchange one currency for another using exchange rates. As a market, forex is influenced by a plethora of factors and key players, including central bank policies, supply and demand, and economic reports.
FAQ
The forex market is where traders trade one currency for another using over-the-counter (OTC) markets. Exchange rates vary from one currency to another, meaning your profitability depends on how accurately you predict a currency’s rise against another’s decline. The forex market is highly liquid, meaning all transactions are finished quickly.
Currency pairs are traded over the counter, meaning no centralized exchange operates the forex market. You can sign up for a forex trading account with a broker and start immediately trading online. You can trade on major exchanges around the world, such as in New York, Sydney, London, or Tokyo.
Forex trading is about knowing when and by how much a currency will rise or fall in value relative to another currency. It’s also about analyzing fundamental data, such as economic reports and central bank policies. Moreover, technical analysis of data and price movements is necessary.
Yes. Depending on the strategy you use and your risk tolerance, you can make huge gains in forex, even at the slightest price movements. The answer to the question, “What is forex trading and how does it work?” is only the beginning; learn to strategize to be profitable.






![How to Find Someone’s Tinder Profile? [2024 Expert Guide]](https://review42.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/06/Finding-Someone-on-Tinder.jpg)

